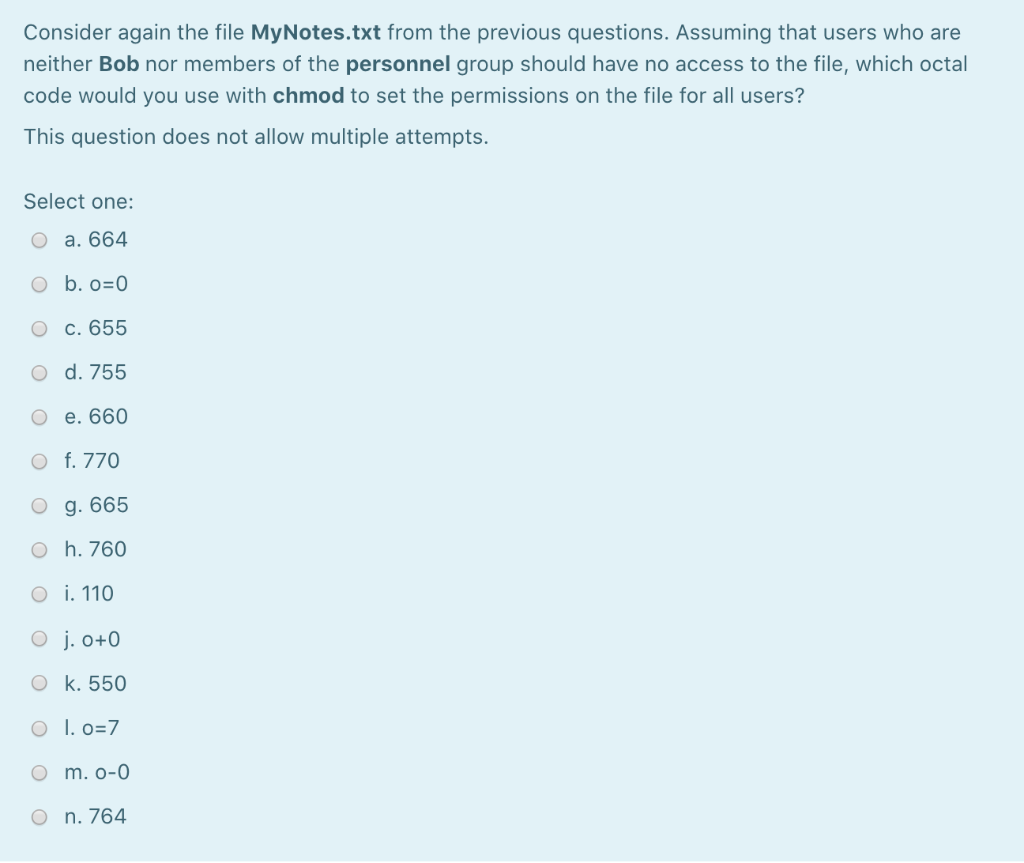
Chmod Numbers Codes

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
Upload Large Files Or Die Trying Perishable Press

Software I Utilities And Internals Ppt Download

104 5 Manage File Permissions And Ownership Lpic1 Exam Guide
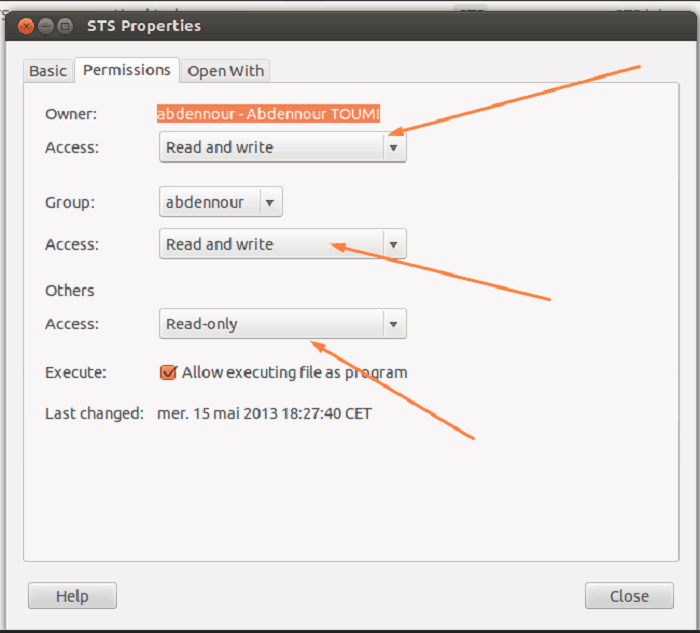
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe.
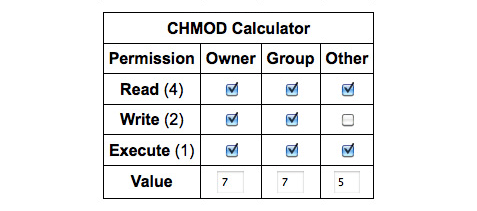
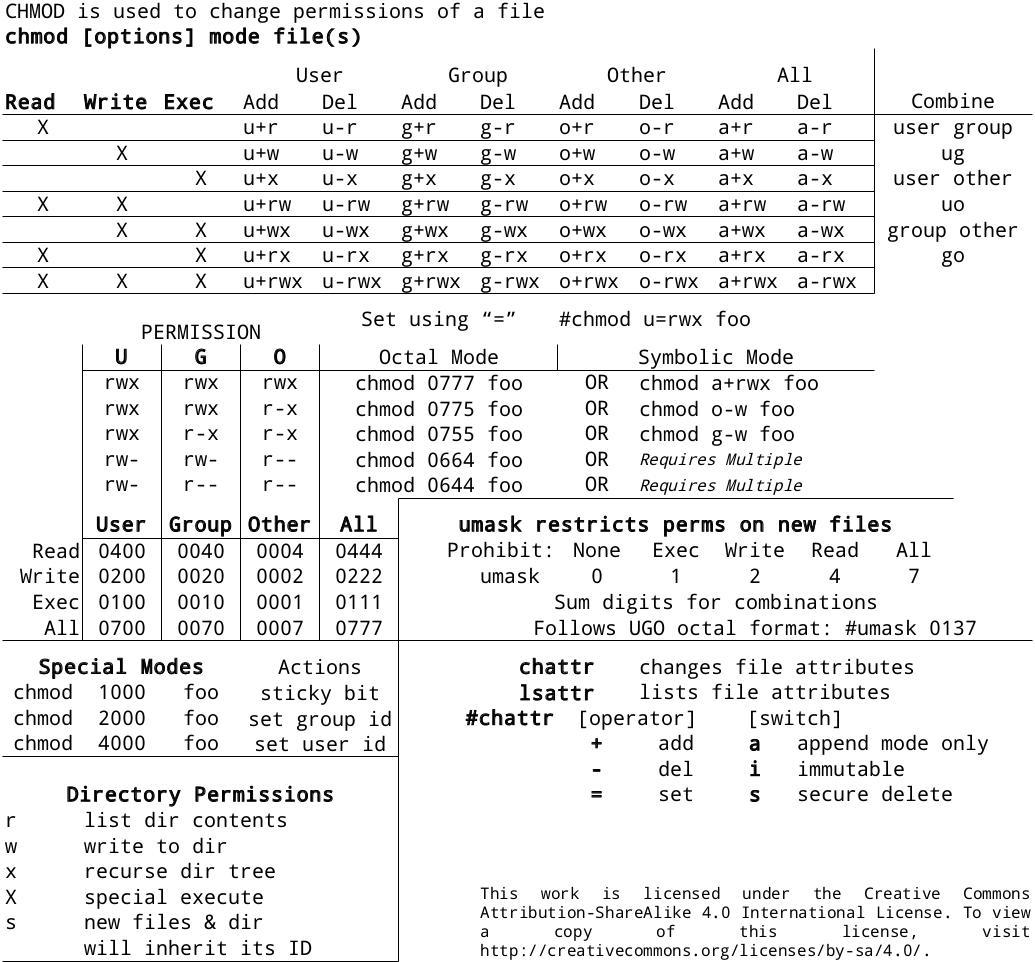
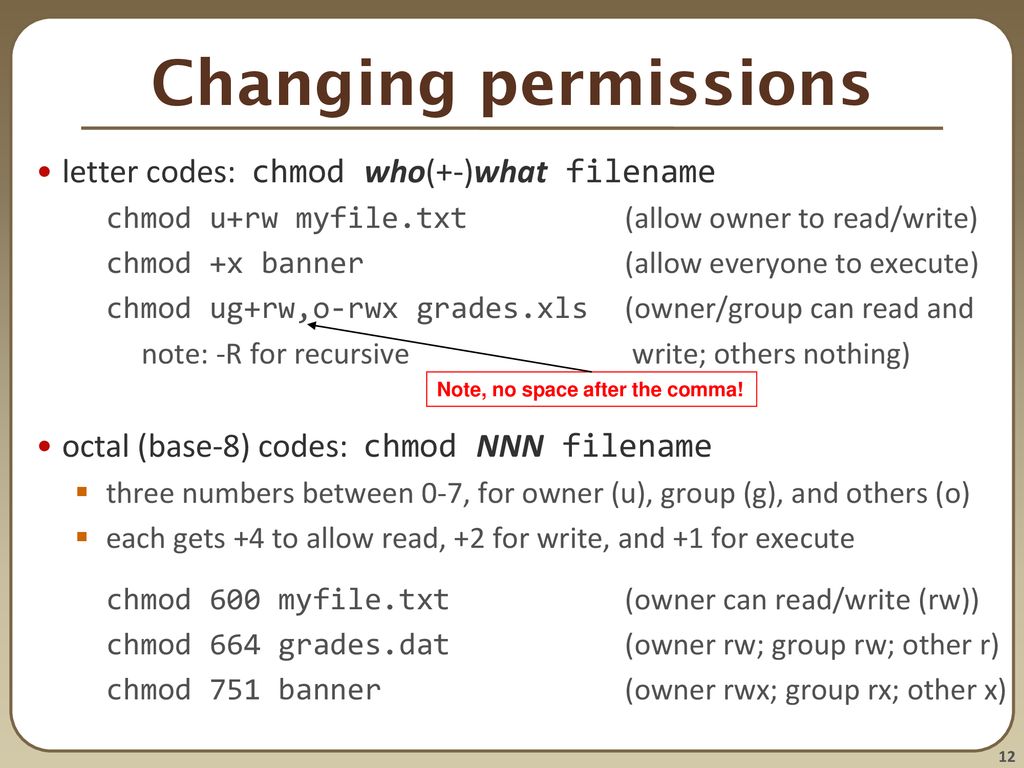
Chmod numbers codes. That’s why a unix admins will say stuff like mode 755 and the bits magically. The digits you can use and what they represent are listed here:. Using chmod with Absolute Permissions.
At the end of this script I need to do a "chmod" on all those files. If you did not set this yourself please do not alter it. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:.
Here are some numerical chmod command examples. Chmod 444 file- Allow read permission to owner and group and world chmod 777 file- Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. Set UID bit - Run the file as the owner regardless of which user is running it;.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and stickyflags. The chmodnumerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
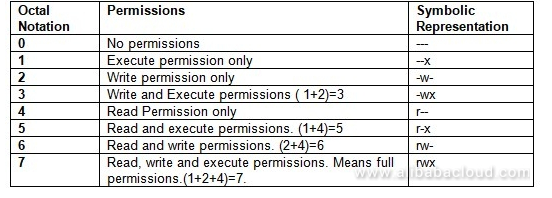
To make your life easier, write the permissions grouped into sets of three letters. (101) Read and execute permissions. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g.
R (read) = 4;. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file. UNIX / Linux chmod command.
The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. Add up these numbers to specify needed rights. Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation.
W (write) = 2;. Here’s how it works:. When using numerical chmod commands you use a sequence of three numbers, and the numbers again correspond to the user, group, and owner of the file.
Allows the owner to write. It stands for change mode. There are 2 ways to use the command - Absolute mode;.
The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons. It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. Each row has 2 examples, one for setting that permission for a file, and one for a directory named ‘dir’.
(011) Write and execute permissions. I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes:. Chmod with Numbers Usage:.
Chmod {options} filename Owner, Group and Other is represented by three numbers. Using the numbering scheme, the chmod command has three number places, for example 744, representing the three user types. Chmod is a command to change permission of a file.
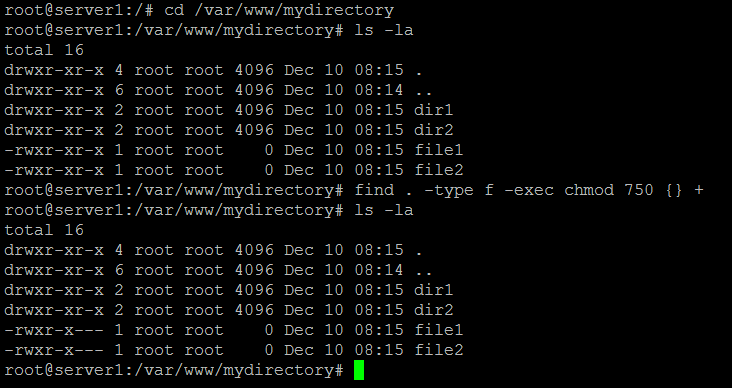
The table below gives numbers for all for permissions types. -type f -exec chmod 640 {} \;. The number “775” is to provide permission to the file.
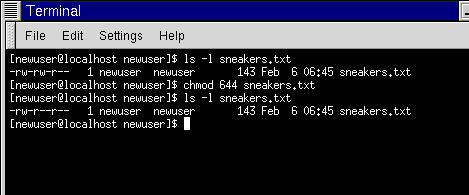
In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone. 777 or -rwxrwxrwx - for files that are written to by all. For instance, let’s look at the test.txt file that we symbolically configured with the chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r test.txt command.
All of them are listed in man chmod, but I will type them out here as well. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. The permission description can be in the form of a number that is exactly three digits.
Chmod +x or chmod a+x:. Here is another way to look at how we come to that number:-(rw-) (rw-) (r--) -(42-) (42-) (4--) 6 6 4. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
/home/user> ls -l foo-rwx--x--- 1 user user 78 Aug 14 13:08 foo /home/user> chmod go+r foo /home/user> ls -l foo-rwxr-xr-- 1. Each digit is a combination of the numbers 4, 2, 1, and 0:. Chmod 001 file- execute by world To combine these, just add the numbers together:.
A bit mask created by ORing together zero or more of the following:. Adding the numbers in each section results in permissions of 664. The full permissions mode number is a 4-digit octal number, though most of the time, you only use the 3 least-significant digits.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. Chmod codes cheat sheet How to use chmod codes in UNIX:. Each digit of this number is a code for the permissions level of three types of people that might access this file:.
There's actually 4 attribute sets you can work with via chmod. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. It allows people to write 777 and get the.
In case it matters, the system is running Red Hat Linux 5.4. $ chmod 400 sample.txt Read by group only $ chmod 040 sample.txt Read by anyone $ chmod 004 sample.txt Write by owner only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by group only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sample.txt Execute by anyone. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level ….
X (execute) = 1;. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change mode.
The atoi() function only translates decimal, not octal. I can't find how to specify which group I want to give these permissions to. 4 stands for "read",.
If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e. When 3 digits number is used, the first digit represents the permissions of the file’s owner, the second one the file’s group, and the last one all other users. Getfacl {dir/file} to get more info on what is set setfacl -b {dir/file} to remove ACL.
No permissions = 0. Enter a three-digit code to see the effect on the permissions. Chmod -R o-r *.page Numerical Shorthand.
Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you make the file readable. To get the value for the options determine the type of access needed for the file then add. The NUMBER can be a 3 or 4-digits number.
Get code examples like "ubuntu chmod codes" instantly right from your google search results with the Grepper Chrome Extension. You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod -R 775 directory Files and directories can have permissions applied independently through the find command. I believe I should run chmod 771 -R directoryname in the parent directory.
Bash, Shell, Terminal, Command Line cheat sheets linux Ubuntu. Chmod by the Numbers. -type d -exec chmod 750 {} \;.
The chmod command uses as an argument a string which describes the permissions for a file. You should totally avoid it. For files and find.
Chmod 4555 equates to the following:. Now, it's easy to convert text (ASCII) to binary with our tool. In this mode, file permissions are not represented as characters but a three-digit octal number.
Linux File Permission :. It turns out that you can also set the mode numerically. Both Octal and symbolic modes.
The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. There are three types of permisions in files and folders in unix Read (r) Write (w) Execute (x) And, there is a clasificacion of users called UGO (explained bellow):. 500 to more than ).
Up to this point, we’ve been setting the mode with letters. Chmod testfile -rw-r--r--testfile Enter a combination of r, w, x, and - to see the corresponding numeric code. Special, User/Owner, Group, and Others in that order, when working with the four-number chmods, with that first number being special bits that can be set.
Set the permissions for a file or directory by using the chmod command. Often after downloading an executable file you will need to add this permission before using it. Write the permissions you want the file to have.
# alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. The first number on the left side is for "user", the middle one is for "group" and the right hand one for "other." Now, here's what each number does:. U = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit.
Chmod 777 is considered potentially dangerous because you are giving read, write and execute permission on a file/directory to everyone (who is on your system). Because unix was written a long time ago (in computer years, at least), people who used it were fairly geeky and thought nothing of slinging binary, octal and hex around. 755 or -rwxr-xr-x - directories are usually given this value.
The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file.An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:. Each write, read, and execute permissions have the following number value:. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. 777 or -rwxrwxrwx - directories that have files created inside them. U ~> User (usually, you) G ~> Group (eg sudo group) O ~> Others;.
Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. Probably one of the most used case of chmod is to give a file the execution bit.
When you run $ ls -l your output will be something like this:. Add read permission to the owner of the file foo.txt :. Allows the owner to read.
Select the permissions you require below. Chmod for great number of files Hi all, I have a script who generate as an output a lot of files (the number is highly variable :. As you have to define permission for each category (user, group, owner), the command will include three (3) numbers (each representing the summation of privileges).
The + indicates that the file has an Access Control List (ACL) with additional permissions. Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others.
To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone. For example, to add execute. I'm personally in a number of groups, and in a bunch I don't know about as root.
Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. For octal conversion, use strtol() (or, as Chris Jester-Young points out, strtoul() - though the valid sizes of file permission modes for Unix all fit within 16 bits, and so will never produce a negative long anyway) with either 0 or 8 as the base. You can also read more about modes on Unix systems with 'man 1 chmod' and 'man 2 chmod'.
Chmod 000 testfile << chmod by the Numbers:. Chmod ugo+rwx or chmod u-rw or chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx or a=rwx (a means all) At the risk of scaring with a short shell script, it is possible to view all the permissions minus the sticky bit, the SetGUID bit, and the SetUID bit using some loops:. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
Chmod 754 myfile Here the digits 7, 5, and 4 each individually represent the permissions for the user, group, and others, in that order. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g.
It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically. The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner. (110) Read and write permissions.
Typical Chmod Permissions Values 644 or -rw-r--r-- web pages and images viewed by surfers.666 or -rw-rw-rw- - log files or pages to which are written.755 or -rwxr-xr-x - perl scripts to make them executable. Add up each group in the permissions string, taking r=4, w=2, x=1.

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
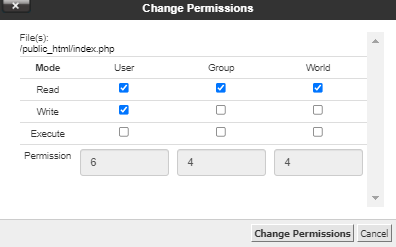
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
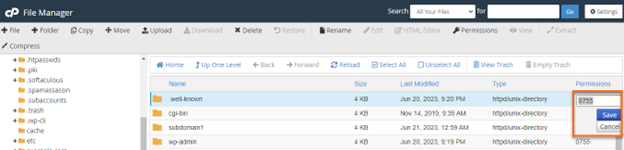
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Tweaking4all Com Chmod Calculator Set File Permission With Chmod

Wordpress Update Fails With A Permission Denied Error Wordpress Development Stack Exchange
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Chmod Permission On Bash Install Issue 38 Sdrausty Termux Archlinux Github

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather

Understanding File Permissions

File Permission In Linux Chmod Command Armantutorial
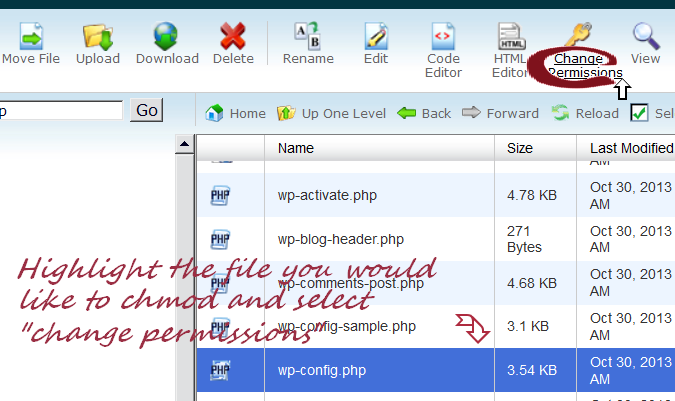
Chmod File Permissions Crosswinds Cadre

Linux Chmod Calculator Chmodcalculator

Shell Programming Ppt Download

How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source
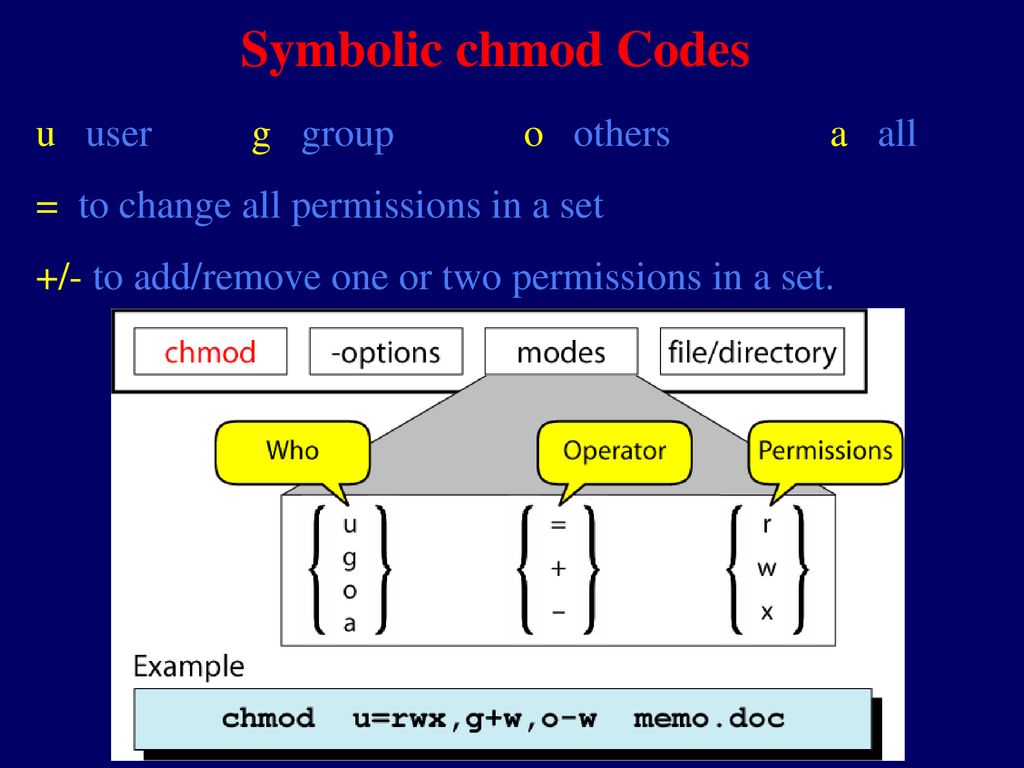
Security And File Permission Ppt Download
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Os Mkdir And Os Mkdirall Permission Value Stack Overflow
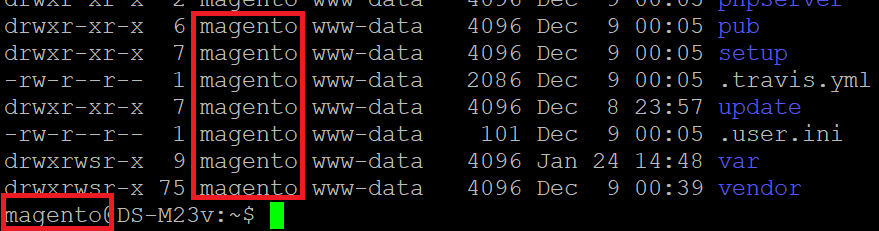
About Chmod Issue Setup Magento 2 Beginner Tutorials Reviews And Discussions

Solved File Permissions In Unix Command And Python I Hav Chegg Com
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Solved Options For Process A File1 File2 File3 Options Chegg Com

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
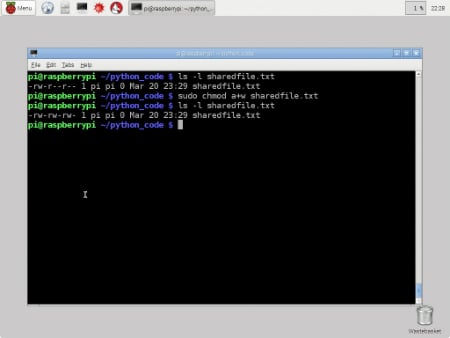
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies
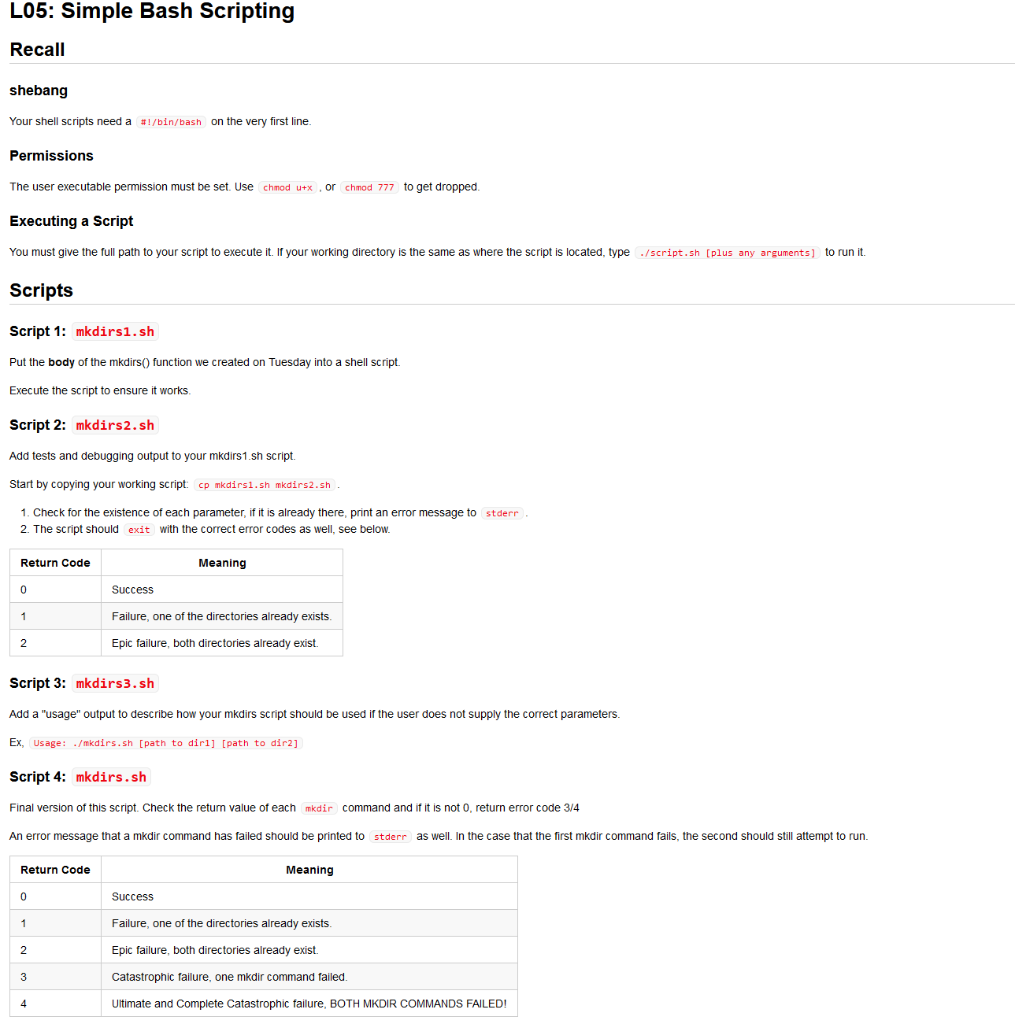
L05 Simple Bash Scripting Recall Shebang Your She Chegg Com

Codepen Chmod Translator

Chmod Wikipedia

Recommended File Permissions For Wordpress Asdqwe Dev

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Linux Operating System Computer Security

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Develop Paper

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command 1 Vichhaiy Welcome
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqtj7hmhwhqltb Dg3vru7pifk7qn5xlkqq4c3n1r24dp3rp4d Usqp Cau

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Foundation Topics Exploiting Local Host Vulnerabilities Exploiting Local Host And Physical Security Vulnerabilities Pearson It Certification

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today
0xax Chmod Cheat Sheet Linux Cli Http T Co B5yd7pk1

Pdf Chmod Cheat Sheet Sunny Yiu
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Chmod C Xv6 Chmod Test Program Need Help Completi Chegg Com
Chmod C Xv6 Chmod Test Program Need Help Completi Chegg Com

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Chmod Or File Permissions Code Blog Perlubantuan Portal
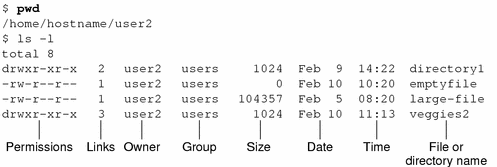
File And Directory Security Solaris Advanced User S Guide

Posted Withrepost Terminalworld It Is The First Column In The Output Of Ls L Command Which Tells All About The Permissions Very Interesting And Importan Linux Linux Permissions Software Engineer

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Solved Question 23 1 Point Message Authentication Code Chegg Com

Unix Permissions Explained

Unix Permissions

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Chmod

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Solved 1 Quick Connect Profiles Problem 45 Time Left Chegg Com

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Basic Linux Commands For Beginners Linux Maker Pro

Unit 2 Resource Management In Linux Ppt Download
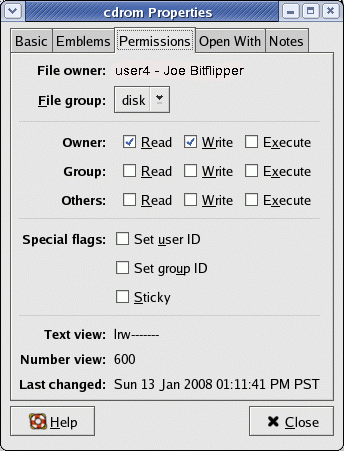
Linux Tutorial Managing Group Access On Linux And Unix
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Ebwotxar3ehy2m
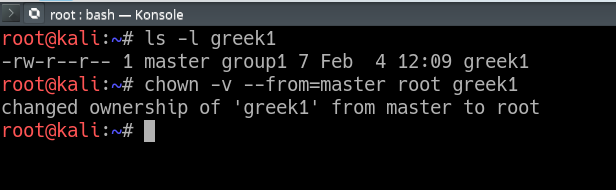
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Persistent Shell Settings Users Groups Permissions Ppt Download
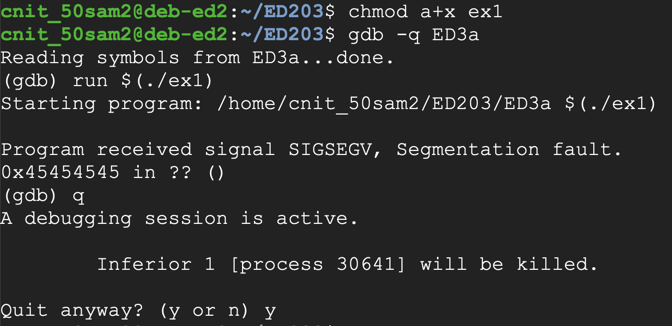
Ed 3 Linux Buffer Overflow With Listening Shell 15 Pts 30 Pts Extra

Umask Wikipedia
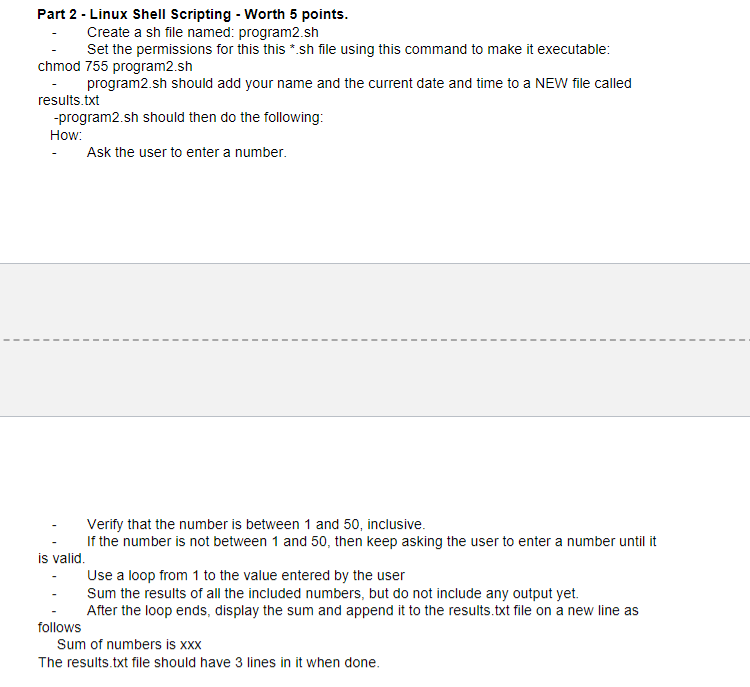
Solved Please Follow Each Rules For Coding Carefully Ple Chegg Com

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

Chmod Numbers

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora

Demystifying File And Folder Permissions

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
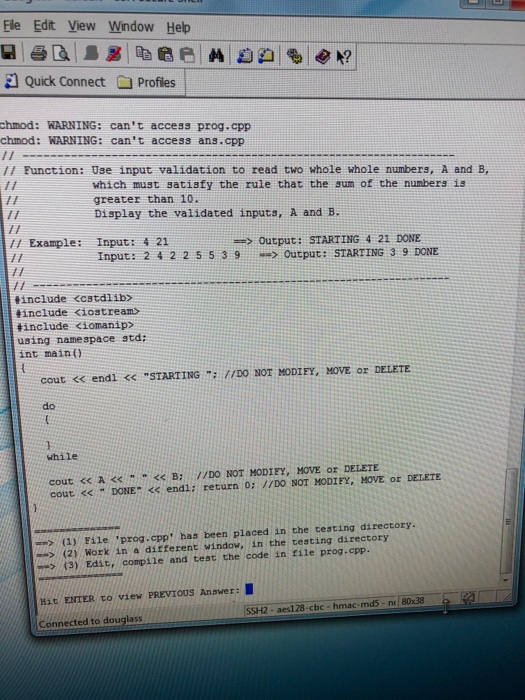
Solved Fle Edit View Window Help Quick Connect Profles Ch Chegg Com

Linux Users And Groups Linode

10 Terminal Commands That Will Boost Your Productivity
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
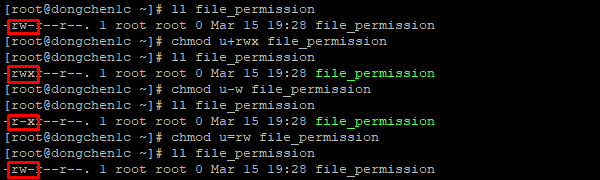
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux Commands Frequently Used By Linux Sysadmins Part 4

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
Www Doralacademyprep Org Ourpages Auto 15 12 7 Chmod 15 16 Jr 1 student Pdf

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft



